LiDAR for cars: autonomous driving and the technology of the future
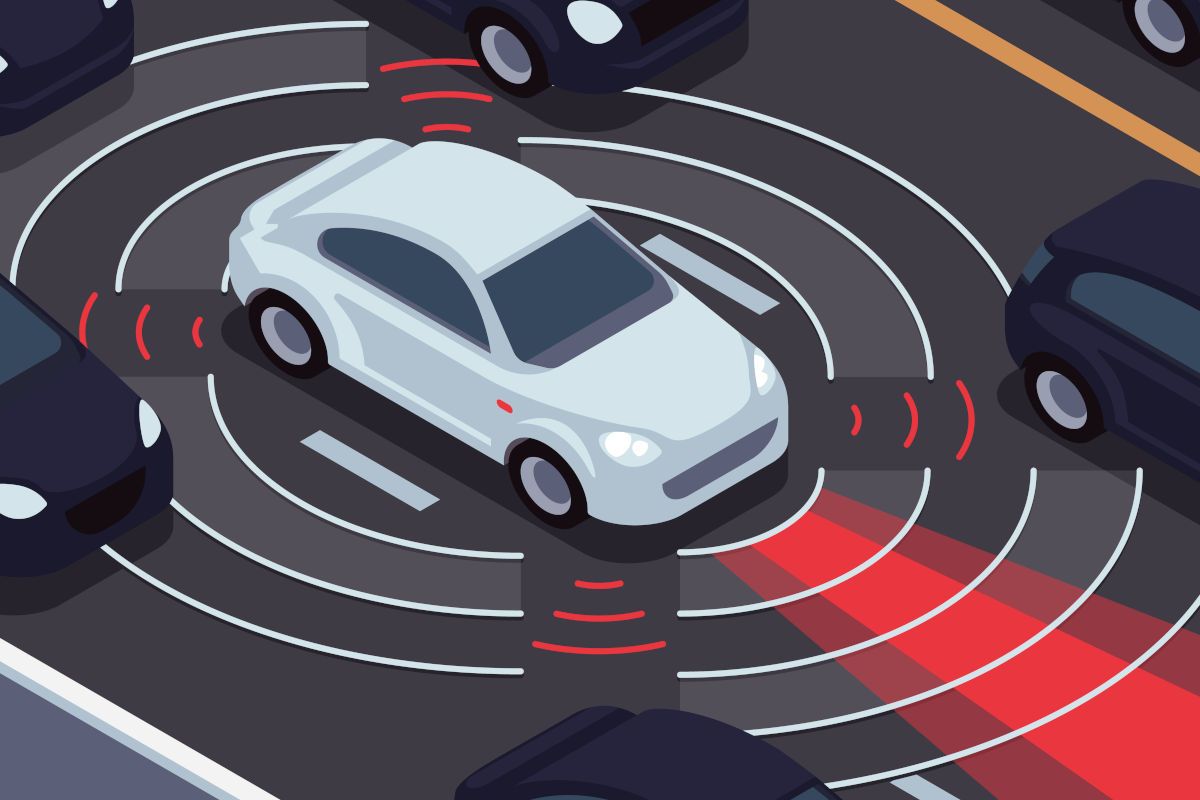
Autonomous driving is an area that demands and produces groundbreaking technology. This includes Light Detection and Ranging - LiDAR for short. This advanced sensor technology has the potential to take autonomous driving to a new level and enable safer and more efficient mobility in the future – after all, it is the third main sensor in autonomous vehicles alongside radar and cameras.
On this page, you can find out everything you need to know about LiDAR for cars and the possibilities that this advanced technology offers for autonomous driving.
How LiDAR works in cars
LiDAR systems have complex sensors and a large number of hardware components, but have a very simple operating principle: similar to a radar, LiDAR sensors emit laser pulses that are reflected by the environment and measured by the system.
Exact distances can therefore be calculated using the time-of-flight measurement (the time between the laser being emitted and the reflection being picked up by the detector). If the LiDAR sensor on the car emits this pulse a thousand times or more, an exact map of the surroundings is created that also captures details. This allows the vehicle to orient itself and adapt its driving behavior to different road users.
LiDAR sensors are used in various assistance systems for autonomous driving, e.g. in adaptive cruise control, real-time perception or lane departure warning systems. LiDAR is even a popular tool for measuring buildings.
Among the different types of LiDAR (presented below), several approaches can be distinguished, namely:
Direct-Time-of-Flight-LiDAR (dToF)
dToF or direct-Time-of-Flight-LiDAR is a simple approach that uses an infrared laser pulse, a receiver and a timer. The LiDAR system emits a pulse that starts the timer. As soon as the echo is received, the timer stops and the transit time is measured.
Using the known speed of light, the distance to the object can be calculated accurately. A useful feature of dToF is the ability to receive multiple echoes and thus detect multiple objects. This technology is extremely flexible and precise and can accurately measure distances from a few centimeters to several hundred meters.

Indirect-Time-of-Flight-LiDAR (iToF)
In the case of indirect ToF lidar (iToF), a continuous light wave is emitted by the laser. The phase of the emitted beam is compared with the echo beam to determine the distance.
Although iToF is widely used, its limitations become apparent at short distances of up to ten meters. It is also unable to cope with multiple objects, as only the strongest echo is detected.
LiDAR systems are not flawless. Each type of lidar system has its strengths and weaknesses. For example, rotating LiDAR systems are ideal for quickly detecting large areas, while scanning LiDAR systems enable precise measurements of nearby objects. LiDAR is now even built into the iPhone.
FMCW (Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave) LiDAR
ToF lidar (time-of-flight lidar) works excellently at night, but has its weaknesses. For example, in bright daylight it is often disturbed by sunlight in the infrared range, which generates additional noise when receiving signals.
This is why FMCW LiDAR is a very important option. This LiDAR system works by means of optical signal pre-processing, which suppresses incoming background radiation and interference, making the signal clearer.
Good to know: With the help of LiDAR, the self-driving Ford Fusion model was able to drive at night without headlights. The test site was a desert road.
Find out more about intelligent traffic solutions: Intelligent transportation systems
These LiDAR systems are to be used in cars
LiDAR was already in use before the advent of autonomous driving. The technology was developed in the 1960s for surveying and mapping work and was used to measure terrain heights, for example. With the advent of autonomous driving, LiDAR also gained importance for the automotive industry.
LiDAR plays a particularly important role in the safety and reliability of autonomous driving systems. The technology is used in various driver assistance systems and is also used to support fully autonomous vehicles in making decisions in road traffic. The following LiDAR technologies are to be used in the future:
In addition to LiDAR, a reliable infrastructure is another basic prerequisite for greater road safety. Modern road markings play an important role here.
Mechanical Scanning LiDAR
This type of LiDAR uses a rotating mirror or prism to direct the beam in different directions. The laser pulses are emitted in a sweeping motion, covering a specific field of view.
Solid-State-LiDAR
Solid-state LiDAR systems use a method in which the laser beam is directed onto the same field of view and fanned out – without the use of mechanically moving scan components. Without these moving parts, solid-state LiDAR systems can be installed much more compactly and robustly than conventional sensors.
The non-moving systems also offer the advantage of faster scan rates, lower energy consumption and greater reliability than mechanical LiDAR scanners.
3D-Flash-LiDAR
Flash-LiDAR relies on a single laser pulse that captures the entire field of view in a brief moment. The measured time of flight of the light reflected to the sensor is used to create a comprehensive 3D image of the surroundings in just one shot.
Flash LiDARs are characterized by their high speed and are ideal for real-time applications. However, there may be limitations in terms of range and resolution that should be considered.
Good to know: Lasers that work with a wavelength of 1064 nm in the infrared range are often used for 3D flash lidar methods. In this way, signal overlay caused by direct sunlight can be avoided.
Photon-Counting-LiDAR
Photon counting LiDAR systems use the detection of individual photons that are reflected by the environment. They have an extremely high detection sensitivity and make it possible to create high-resolution mapping and carry out precise distance measurements. Photo-count LiDARs are frequently used in scientific research, for example in photon counting computed tomography.
There are already several companies working on LiDAR sensors: companies such as Bosch, ZF, Velodyne, Luminar, Blackmore, Opsys, Innovusion Quanergy and many others are busy producing and further developing LiDAR systems.
Who uses LiDAR?
The above-mentioned companies such as Velodyne LiDAR, Quanergy, Innovusion and Luminar Technologies, which have established themselves as leading manufacturers of sensor technology, are focusing on the further development of LiDAR systems in order to establish them for autonomous vehicles in road traffic. Luminar, for example, specializes in the development of high-performance LiDAR systems for autonomous vehicles. Luminar's customers are none other than Mercedes and Audi.
Manufacturers such as Audi, BMW, Ford, Volvo and Waymo are not the only ones to have recognized the potential of LiDAR. Tesla, one of the pioneers in autonomous driving, is now also relying on the advanced sensor technology – and this after Elon Musk had previously described LiDAR as a "mistake".
Concrete Solutions by SWARCO
Conclusion: LiDAR for autonomous vehicles has a future
LiDAR for cars is undoubtedly promising for the field of autonomous driving. As a crucial component of sensor technology, LiDAR enables precise depth perception and thus creates the basis for safe and efficient mobility in the future.
Through continuous development and the efforts of companies to improve LiDAR systems and make them more cost-effective, we will see even more powerful and reliable solutions in the near future. LiDAR is and will remain a crucial building block for the further development of autonomous driving and will have a significant impact on the mobility of tomorrow.
Last but not least: Autonomous driving will bring many advantages in the future and, above all, greater safety. An important component of this safety is not only networked traffic systems, but also state-of-the-art sensor technology such as LiDAR. It can increase road safety, support decision-making in autonomous vehicles and improve traffic flow.
FAQ
LiDAR sensors use laser pulses to detect the environment and measure the time of flight of the reflected signals. These measurements are used to create a precise 3D point cloud of the surroundings, which also enables depth perception. Obstacles can therefore be reliably detected.
Depending on the system, LiDAR can have a short or long range. Ranges of just a few meters are possible, as well as ranges of 200 meters. The LiDAR system developed by AEye even has a range of up to 1000 meters.
LiDAR has moved into the affordable range. They are currently available for less than €10,000, but significantly lower prices are possible in the future. If this prediction becomes reality, LiDAR could be installed in cars as standard.
Many manufacturers are now dedicated to the production and further development of LiDAR sensors. These include well-known companies such as Bosch and Velodyne, as well as Luminar, Blackmore, Opsys, Innovusion and Quanergy, to name but a few.

STAY INFORMED
GET OUR NEWSLETTER!
Subscribe to our ITS / Smart Mobility Newsletter and receive regular updates on trends, developments, solutions and events.
Bilder: © MicroOne – stock.adobe.com; © Mopic – stock.adobe.com; © Windawake – stock.adobe.com





